|
|
Location: GUIs >
Windows >
Windows NT 3.51 . . Windows NT comes in two different forms, Windows NT Workstation and Windows NT Server. Both are the same operating system, however licensing and packaging are different. Windows NT Server gives more priority to server processes, uses a licensing agent, and comes bundled with additional server software programs. Windows NT Workstation gives user applications more priority and limits the number of simultaneous network connections to 10 users. Despite its Windows 3.1-ish look, Windows NT is a new protected mode 32-bit multi-threaded operating system. Underneath the hood Windows NT is almost completely unrelated to the other "Microsoft Windows" product. Windows NT can run well behaved DOS and Windows 3.x applications by using a special emulation sub-system. Windows 3.1, being a 16-bit cooperative multitasking operating system can not run Windows NT applications directly. A "Win32s" subsystem was made available for Windows 3.1 that allowed it to run Windows NT applications that made use of only a very small subset of API commands. These applications therefore could not use multi-threading or other advanced features which were simply not possible in Windows 3.1. Windows 95, however, integrated the majority of the Windows NT APIs in to the framework of Windows 3.1.
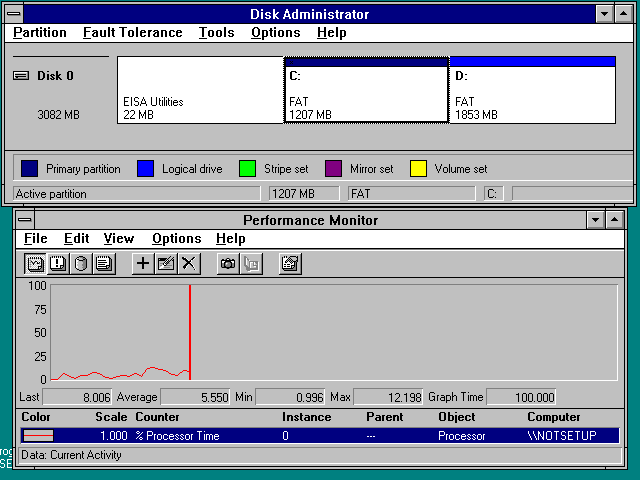
Performance is important in Windows NT, therefore it includes a graphical performance monitor that allows the activity of core parts of the operating system to be logged and displayed. |